Construction sites involve a large number of vehicles — from heavy machinery like excavators, cranes, and concrete trucks to support vehicles such as service vans, trailers, and small utility trucks. Managing this fleet effectively is critical, but traditional methods (manual check-ins, paper logs, visual inspections) are often insufficient. RFID technology offers a transformational approach, giving construction companies much greater visibility, control, and operational efficiency.
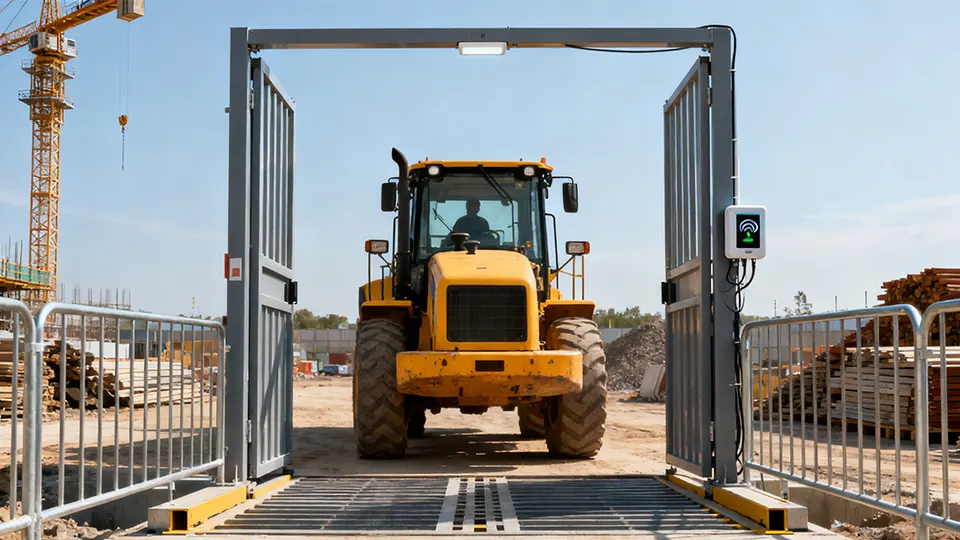
With RFID, every vehicle can be uniquely identified and tracked automatically. When a vehicle equipped with an RFID tag passes through a checkpoint — such as a gate or yard entrance — readers record its identity and time. This automated logging provides real-time data on movements, enabling managers to know precisely which vehicles are on site, how long they stay, and when they leave. Such insights dramatically improve control over site operations: only authorized vehicles can enter restricted or hazardous zones, and any unexpected departures or entries can trigger alerts.

Beyond security, RFID enables much better utilization of the fleet. Fleet managers gain a clear picture of utilization patterns — which vehicles are most active, which sit idle, and where the bottlenecks occur. With this data, they can reassign vehicles more intelligently, reducing idle time and potentially postponing the purchase of additional units. Maintenance also becomes smarter: because every vehicle’s usage is logged, maintenance scheduling can be based on actual work cycles rather than guessed intervals. This usage-based maintenance helps extend vehicle life and reduce costly breakdowns.
Moreover, the system strengthens safety and compliance. Tagged vehicles entering sensitive zones can be strictly controlled; only vehicles with valid credentials or certain tags will be allowed. In case of incidents, the historical movement record offers accountability: which vehicle accessed which area, at what time, and for how long. Over time, the accumulation of this data also supports analytics: construction firms can generate reports on fleet flows, dwell times, peak usage windows, and more — all contributing to smarter planning, better deployment, and cost savings.
The Right RFID Deployment
Putting RFID to work in construction environments requires thoughtful design. Construction sites are tough: vehicles operate in dusty, wet, metallic, and vibrating settings. To succeed, system architects must choose durable tags, field-worthy readers, and a robust deployment plan.
Choosing the Right Tags
For construction vehicles, rugged passive UHF RFID tags are often the backbone. These do not need batteries and can harvest energy from the reader’s signal. Because many vehicle surfaces are metal, on-metal UHF tags are crucial; they are specially engineered to maintain performance when mounted on metal. Some providers also make welded tags for permanent, highly reliable attachment — ideal for heavy machinery, attachments, or permanently-installed components.
Tag selection is a balance: passive tags are cost-effective and maintenance-free, while active tags offer richer data but require battery support. In most vehicle-tracking use cases, rugged passive tags represent the best value.
Infrastructure
A practical RFID deployment combines different types of readers:
Fixed readers: Installed at entry and exit points (site gates, parking areas, lay-down yards), these capture tag reads automatically as vehicles pass through.
Vehicle-mounted mobile readers: A mobile reader can be installed on a service or utility truck, which then drives around the site, picking up tags from parked or idling vehicles. This “reader on wheels” sweeps the area and updates the system without additional labor.
Handheld readers: Rugged handhelds help operators commission new tags, audit tag status, or troubleshoot unread tags. These devices can also be used when verifying or replacing tags.
Backend software: All reader data should feed into a central asset-management platform. This backend assigns each tag to a vehicle, logs all reads, enforces rules (e.g., gate access), and provides reporting and analytics. For optimal results, this platform should integrate with existing construction management systems — dispatching, maintenance scheduling, safety monitoring, and more.
Deployment Strategy
A successful implementation typically follows this path:
Pilot Deployment: Begin with a subset of vehicles and install a few readers (gates / mobile). Use handhelds to test tag readability and placement, then refine.
Tag Installation: Mount tags carefully, using on-metal or welded tags where appropriate. During commissioning, each tag is registered in the system with its vehicle identity and relevant metadata.
Reader Network: Strategically install fixed readers at gates and yard entrances; deploy vehicle-mounted readers on a sweeper vehicle to scan assets across the site.
System Rules: Define business rules in software: which types of vehicles may access which zones, alert thresholds, and reporting criteria.
Training: Provide training to security personnel, drivers, fleet managers, and other stakeholders. Emphasize the system’s business value (security, utilization, efficiency), not just surveillance.
Maintenance & Audit: Periodically scan tags with handhelds to check readability. For active tags, monitor battery levels and replace as needed.
Continuous Optimization: Use the collected RFID data to drive continuous improvement — refining tag placement, adjusting rules, optimizing vehicle assignments, and improving throughput.
Industry Benefits and ROI
The true power of RFID for construction-site vehicle management becomes clear when viewed through real applications and the tangible returns that companies achieve.
By deploying RFID for vehicles, construction firms can realize multiple benefits:
Loss Reduction: Unauthorized vehicle movement is minimized. Any unexpected departures are logged and flagged, reducing asset shrinkage.
Improved Utilization: Real-time visibility means fleet managers know where every vehicle is and can allocate them efficiently — thus reducing idle time and avoiding unnecessary purchases.
Smart Maintenance: Usage-based maintenance extends vehicle longevity and lowers downtime. Rather than following fixed schedules, maintenance is triggered by actual usage data.
Labor Saving: Automation of check-ins and check-outs at gates removes the burden of manual record-keeping, freeing up security and administrative staff.
Safety and Compliance: By tying RFID data to site access rules, only approved vehicles can enter restricted areas. In emergencies or audits, managers have a digital log of every vehicle’s movements.
Strategic Insights: Over time, fleet movement data enables analytics: dwell time trends, peak traffic windows, underutilized assets, and long-term fleet planning.
Combined, these benefits often deliver a compelling ROI — the system can pay for itself through reduced losses, better asset use, lower maintenance costs, and lower labor overhead.
Industry Examples
One of the most prominent implementations comes from a leading construction-technology company that introduced an RFID-based system tailored to heavy civil construction. In this system, specialized RFID tags are placed on machine attachments, trailers, and other high-value assets. Vehicles entering or leaving the site pass through fixed RFID gate readers, and a mobile reader mounted on a truck sweeps the site for other tagged assets. All read events feed into a centralized asset manager, enabling real-time tracking, anomaly detection, and detailed reporting. This setup helps deter theft, optimizes asset transfers, and increases utilization.
In another deployment, a construction company used rugged passive UHF tags on its vehicles and machinery, pairing them with durable handheld readers for audits. The system replaced labor-intensive manual inventory processes and eliminated unaccounted asset movement. In addition, managers could schedule preventive maintenance based on actual usage, improving uptime and reducing repair costs.
Technology providers specializing in rugged RFID hardware have also played a key role. They offer hardened, on-metal tags and welded tags that can withstand harsh construction site conditions like moisture, impact, extreme temperature, and vibration. These tags remain readable over long periods, making them ideal for long-term vehicle asset management.
Conclusion
RFID is not just a technology fad — for construction firms managing large, diverse vehicle fleets, it is a strategic asset. By deploying rugged tags, implementing a thoughtful reader architecture (gates, mobile, handheld), and leveraging a backend system for tracking and analytics, companies can greatly reduce loss, improve utilization, enhance safety, and make data-driven decisions.
Many real-world deployments already show strong ROI, with reduced theft, lower idle time, smarter maintenance, and lower labor costs. As construction continues to embrace digitization, RFID-based vehicle management is emerging as a foundational technology. For contractors who want to modernize operations, secure assets, and optimize their fleets, investing in RFID is a powerful move — transforming uncertainty into visibility, and inefficiency into actionable intelligence.