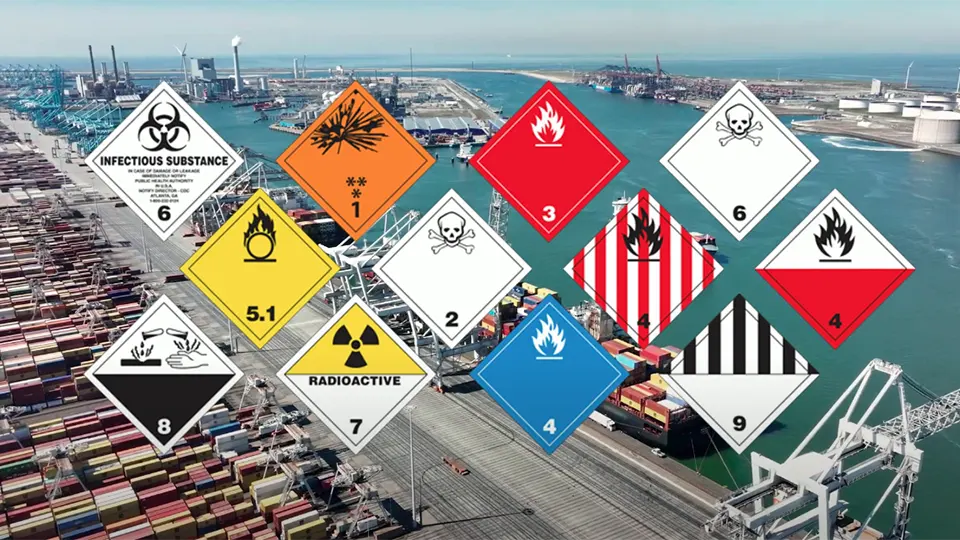
Transporting hazardous materials like corrosives, flammables, or toxic inhalation hazards is a high-stakes business. Human errors, limited visibility, and paperwork delays can lead to serious accidents or violations. RFID brings real-time oversight and robust safety。
Why RFID Matters in Hazardous-Goods Transport
Real-time visibility & safety
RFID tags with GPS, temperature or shock sensors, and wireless communication allow companies to monitor every drum, container, or transport vehicle live.
Error-free data capture
Automating reads removes manual-entry mistakes. Organizations have reported near-perfect read rates tracking chemical drums and tankers, boosting accountability and traceability.
Hands-free compliance in emergencies
During spills or accidents, first responders can scan tags to get critical info instantly—container ID, contents, temperature history, and safety documentation—enabling fast, informed action.
RFID Hardware & Software
A fully effective RFID system combines certified tags, strategically placed readers, and intelligent back-end platforms.
Tags
Long-range tags: These rugged UHF tags are mounted on trailers, tankers, and railcars. They broadcast GPS location and send environmental data such as temperature, shock, humidity, and seal status.
Explosion-proof drum tags: Built for harsh environments, these tags attach to steel drums via strong adhesive or magnets, and provide ID, temperature reading, and tamper detection.
Readers & Antennas
Fixed portal readers: Installed at docks, gate entries, and rail yards, these fixed readers automatically capture tagged items as they move through checkpoint zones like loading or unloading areas.
Truck-mounted or toll-lane readers: Placed on trucks or toll lanes, these readers automatically detect tags when vehicles enter or leave facilities, enabling seamless capture without driver involvement.
Handheld readers: Designed for hazardous environments, these handheld devices allow personnel to perform spot checks near pump rooms, hoses, valves, or other sensitive zones.
Connectivity & Integration System
Central systems, such as asset management platforms or Dangerous Goods Information Systems (DGIS), receive RFID data, verify it against manifest records, trigger alerts when issues arise, and automatically generate compliance documentation.
Rule-based logic fires off alerts—like excessive temperature readings, off-route movements, or seal breaches—and automatically produces chain-of-custody reports, placarding confirmations, and shipment logs.
Step-by-Step Implementation
Here’s how a mid-size hazardous-goods shipper typically deploys RFID with safety and efficiency in mind:
Tag Assignment
Attach the appropriate tag to each drum, IBC, tank, railcar, or tanker. Each tag’s unique ID is mapped to shipment data such as chemical type, batch number, and relevant safety documentation.

Reader Placement
Position fixed portal readers at key points like dock doors, yard gates, and weigh stations to automatically scan tags during loading and unloading events.
Deploy truck-mounted or toll-lane readers to automatically capture data as vehicles enter or exit.
Install trackside readers to detect railcars passing through checkpoints along transit routes.
Connectivity Setup
Ensure all tags transmit real-time data via GPS and telemetry to a centralized analytics platform. Integrate this system with existing ERP, warehouse management, and dangerous-goods compliance systems to enable automated operations.
Alerts and Compliance Configuration
Establish rules so the system notifies stakeholders if a temperature limit is exceeded, a seal is broken, a route deviates, or a checkpoint is missed. Automatically compile chain-of-custody documentation, placarding verification records, and “cleared to ship” statuses without manual intervention.
Training & Testing
Train warehouse staff, drivers, and emergency responders on scanning procedures, tag handling, and protocol during incidents. Conduct drills simulating spills, tampering, or theft to ensure everyone can respond effectively and efficiently.
RFID Hazmat Tracking Applications
Dow Chemical – Railcar Monitoring
A major chemicals company outfitted hundreds of railcars carrying toxic hazmat with active RFID tags featuring GPS and environmental sensors. This setup transmits real-time updates to a centralized system, enabling proactive alerts and fulfilling regulatory oversight requirements.
Drum Tracking Pilot
At loading sites, portal-based RFID arrangements consistently achieved near-100% read rates for tagged 55-gallon drums, even when stacked or packed closely. These successful trials showcased reliability for handling hazardous waste movements and cross-border logistics.
Nuclear Material Transport
In government and research applications, active RFID tags with environmental sensors were used to track nuclear waste drums and secure transport vehicles. These tags transmitted GPS location and sensor readings from vulnerable zones, ensuring safe, monitored travel across long distances.
Refinery & Plant Asset Tracking
Within explosion-risk areas of refineries or chemical plants, certified passive RFID tags and handheld readers were deployed to track hoses, valves, and mobile equipment. This protected workers while maintaining operational compliance during maintenance and inspections.
Final Take
From real-time railcar monitoring to drum scans in tight spaces, RFID systems proven in real-world environments demonstrate that well-equipped, integrated, and trained operations lead to transparent, responsive, and compliant transport. If you’d like more info on specific tag models, reader options, or software platforms, just let me know!